
🚆 System in Numbers
- Lines & Stations: Two lines totaling ~31.6 km (19.6 mi), with 39 stations in all.
- Blue (North‑South): 16.9 km from Menelik II Square to Kaliti, opened 20 Sept 2015.
- Green (East‑West): 17.4 km from Ayat to Tor Hailoch, inaugurated 9 Nov 2015.
- A shared elevated core spans ~2.7 km across CBD.
Origins & Funding
- Built by China Railway Engineering Corp (CREC), with CNR Changchun supplying 41 low-floor trains.
- Cost: US $475 million—85% financed via a loan from China’s Ex‑Im Bank, 15% by Ethiopia.
- Operated by Shenzhen Metro Group under a partnership with ERC.
Technical Specifications
- Gauge: Standard 1,435 mm; electrification via 750 V DC overhead catenary.
- Speed: Designed for up to 80 km/h, operational speeds around 70 km/h..
- Rolling Stock: 41 three-section trams, 70% low-floor; passenger capacity around 286–317 per train.
Purpose & Impact
- Milestones: First light rail in Sub‑Saharan Africa.
- Sustainability: Powered by Ethiopia’s largely renewable energy grid; estimated annual CO₂ reductions ~55,000 t (growing to ~170,000 t by 2030).
- Urban transformation: Reduced average transport speeds from 10 km/h to ~22 km/h; improved job access—employs ~1,100 people.
Challenges & Current Issues
- Reliability woes: As of early 2023–2025, only 15–17 of 41 trains are operational due to maintenance deficits and spare parts shortages.
- Deteriorating conditions: Power outages, vandalism, and theft of infrastructure have led to frequent service disruptions and dusty, broken stations.
- Declining ridership: Daily passengers have decreased from over 100,000 at launch to approximately 56,000 amid service reductions.
- Funding shortfalls: Maintenance costs (~$60 million) strain fiscal capacity; farebox covers only a fraction of operational expenditure .
Recent Developments
- Digital ticketing rollout: In March 2025, select stations began testing digital ticket purchases via the Telebirr app, though paper tickets remain for convenience.
- Expansion planning: Long-term plans include expanding current lines and adding two more, potentially reaching up to 185 km over the next decade.
🚆 Lines & Route Details
- Two main lines across the city:
- Green Line (East–West, Line 1): Runs from Ayat to Tor Hailoch, spanning ~17.4 km with 23 stations (including shared section).
- Blue Line (North–South, Line 2): Connects Menelik II Square (Giorgis) to Kaliti, covering ~16.9 km with 22 stations (including shared section).
- There’s a 2.7 km common elevated section through the CBD (Meskel Square to Lideta) served by both lines, featuring five stations.
🕙 Operating Hours & Frequency
- Daily service begins early: first trains depart around 06:00, concluding around 22:00 (though schedule variations and power-related interruptions occur).
- Weekday frequencies (as of April 2025):
- Green Line:
- Weekdays: 7 trains → ~15‑minute headways; full round trip ~105 min
- Weekends: 6 trains → ~17‑minute intervals.
- Blue Line:
- Weekdays: 8 trains → ~15‑minute intervals; round trip ~120 min
- Weekends: 7 trains → ~17‑minute headways.
- Green Line:
- Peak/off-peak schedules (in early years): ~10‑minute frequency during peak, ~20‑minute during off-peak.
- Note: service is often disrupted by power outages, maintenance issues, and occasional full-line shutdowns.
🎫 Fare Structure & Ticketing
- Distance-based fares:
- 2 ETB for short trips
- 4 ETB for medium distances
- 6 ETB for full end-to-end rides
- Tickets are bought only at kiosks next to stations—never onboard. These are distinctive orange booths.
- Ticket types:
- Single and return tickets available
- No reusable passes yet.
- Payment methods:
- Traditionally paper tickets only.
- In early 2025, digital ticketing trial began at a few stations (Menelik Ave., Tor Hailoch, Hayat, Stadium, Qaliti) using Telebirr app or electronic cards.
- E‑tickets expected to roll out more widely via e‑kiosks and cards.
- Fare increases: No public confirmation on major hikes via light rail; reported raise refers to buses in late 2024.
🧭 How to Ride: Step-by-Step
- Arrive at station, often segregated by location type (elevated, underground, central median).
- Buy ticket from the orange kiosk—specify destination, pay 2/4/6 ETB.
- Enter through controlled gates:
- Ticket may be checked at station entrance or onboard vagaries .
- Board the train:
- Trains are 70% low-floor, seating limited—standing is common.
- Ride safely:
- Avoid rush hours (7:30–11:00 & 16:00–19:00); midday is quieter.
- Beware of pickpockets when crowded.
Addis Ababa Light Rail Map
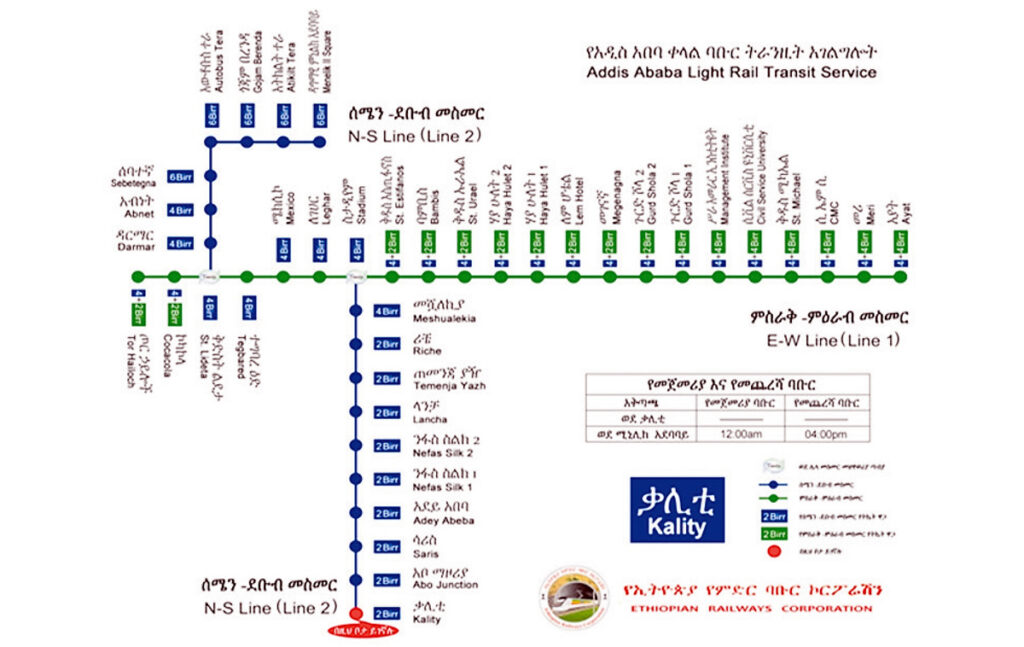
📝 Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Lines | Green (Ayat ↔ Tor Hailoch); Blue (Menelik II ↔ Kaliti); shared section |
| Stations | 39 total |
| Hours | ~06:00–22:00, daily |
| Frequency | 15 min weekdays; 17 min weekends; 10‑20 min historical |
| Fares | 2, 4, 6 ETB depending on distance |
| Ticketing | Station kiosks; digital being piloted |
| Tips | Avoid rush hours, buy ticket before entry, watch your belongings |
The Addis Ababa Light Rail was a groundbreaking start for urban transit in Sub‑Saharan Africa, showcasing the potential for eco-friendly, rapid, and large‑capacity transport. However, its long-term sustainability has been hampered by operational neglect, funding shortfalls, and infrastructure wear. Revival hinges on securing maintenance funding, boosting reliability, and expanding reach to regain ridership and strategic impact.